Whats the Name of the Scale Used to Describe Hurricans
Satellite image of a hurricane named Fran Hurricane Fran was a large powerful destructive hurricane that made landfall near Cape Fear North Carolina on September 5 1996. The scale was developed in 1971 by civil engineer Herbert Saffir and meteorologist Robert Simpson who at the time was director of the US.

How Are Hurricanes Rated The Saffir Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale Explained
The scale used to classify the.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/9115467/harvey_goes_82517.jpg)
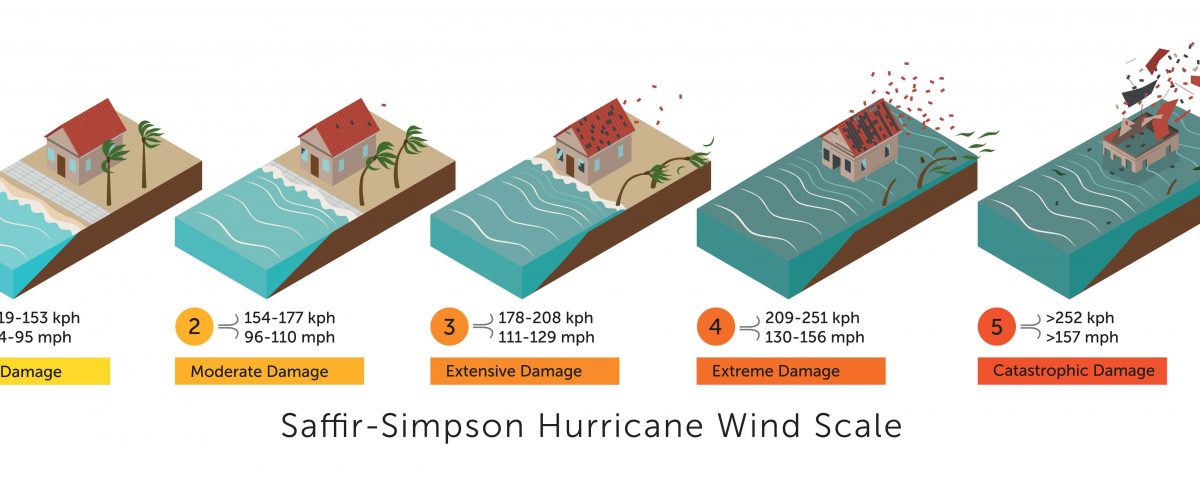
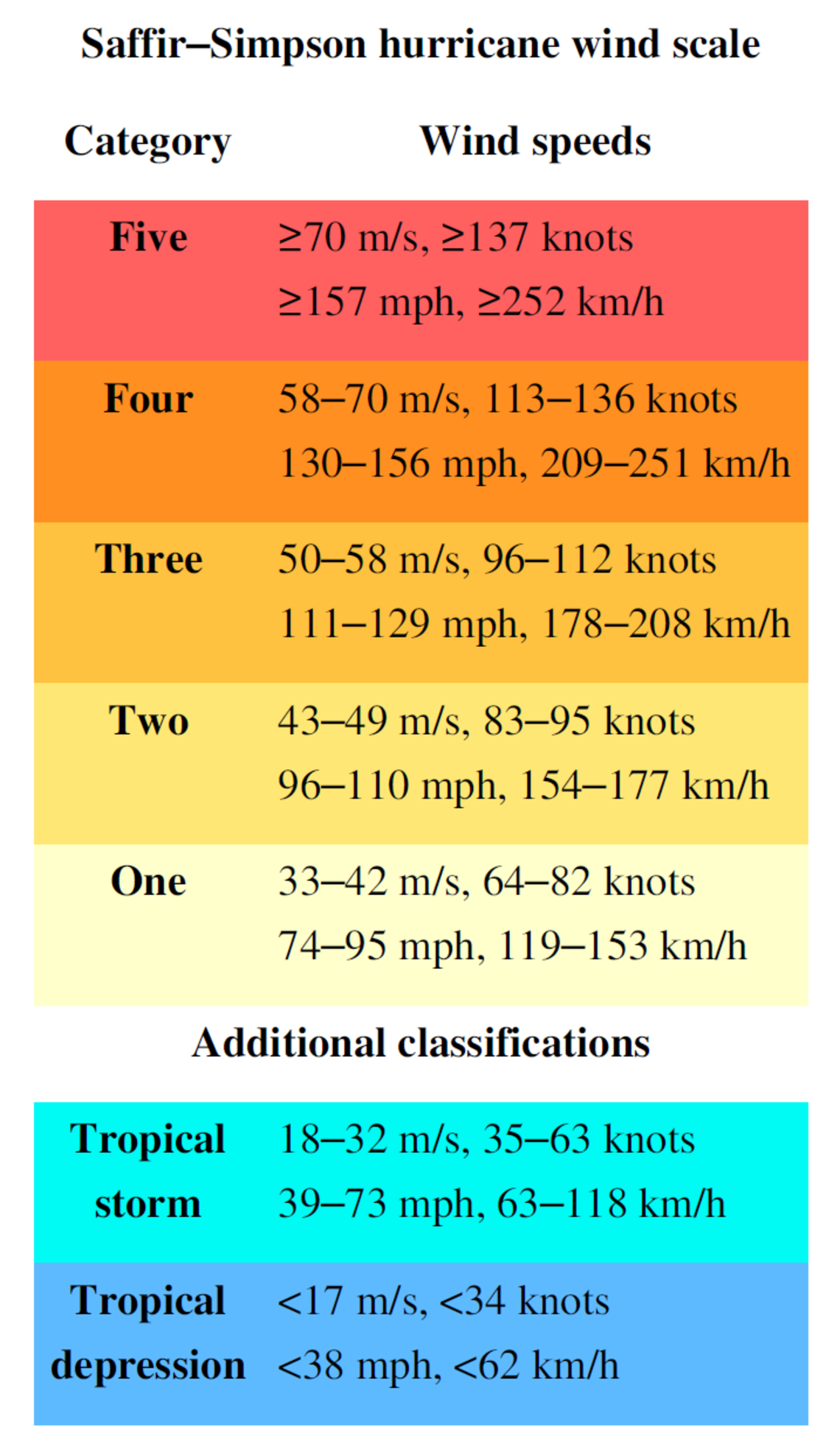
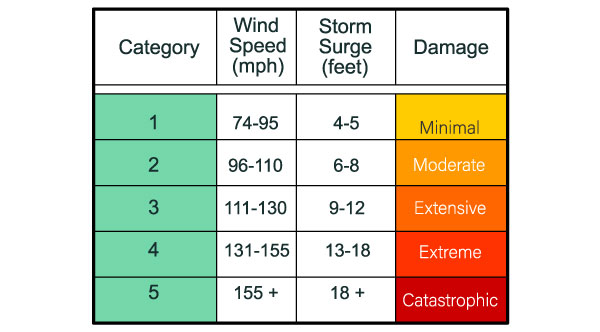
. This scale rates hurricanes from category one to five based on wind speed. The scale was introduced to the general public in 1973 and saw widespread use after Neil Frank replaced Simpson at the helm of the NHC in 1974. The scale used to measure hurricanes is called the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale.
The SaffirSimpson hurricane wind scale is used to classify hurricanes. Winds 96-110 mph 154-177 kmhr. Hurricanes on the other hand are large-scale circulations that are 60 to over 1000 miles across.
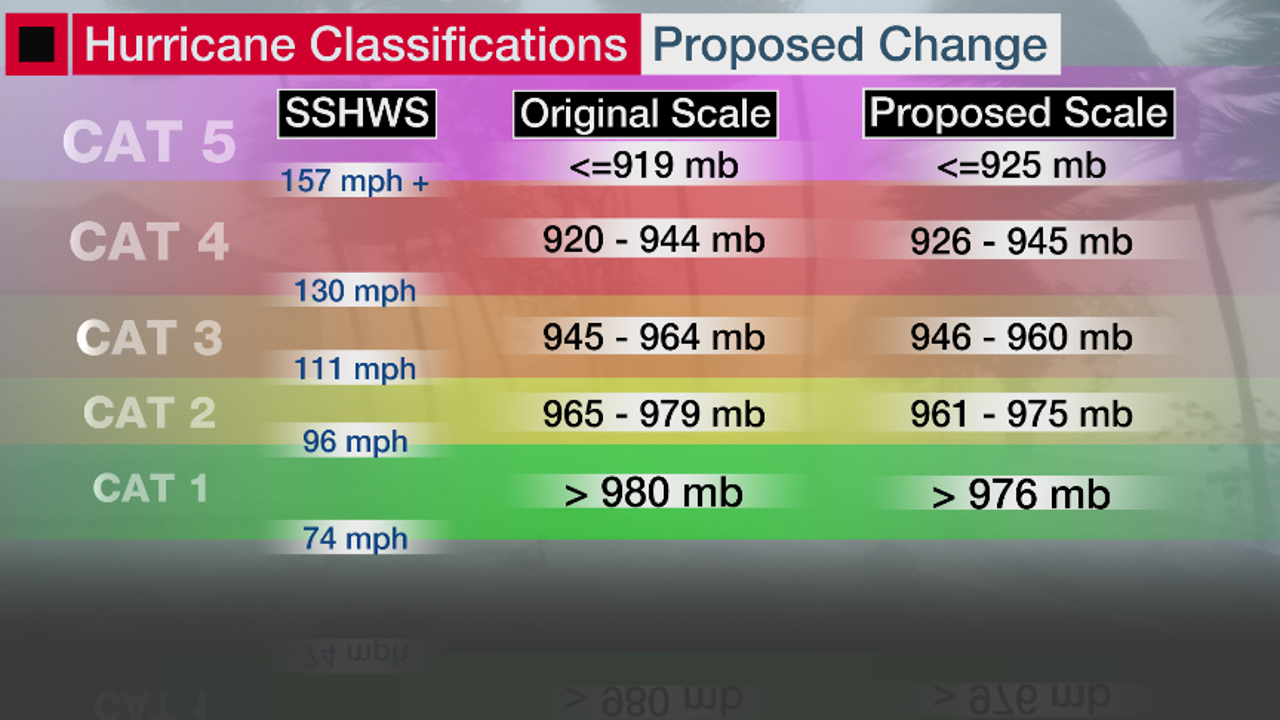
The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale is the standard used to measure hurricane intensity and this year the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration NOAA is making a modification of the scale. Meteorology a wind scale for quite strong wind stronger than a storm. The categories are based on wind speed.
The World Meteorological Organization is in charge of assigning names to tropical storms that originate in the Atlantic Ocean and reach a sustained wind speed of 39 miles per hour. Before the use of short names hurricanes had been categorized by latitude and longitude numbers. Click card to see definition.
The scale of categories is called the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale. Click again to see term. It was introduced to the general public in 1973.
Warm water 80or warmer surface level low pressure upper level high pressure. When a storms maximum sustained winds reach 74 mph it is called a hurricane. The scale starts with 0 and goes to a force of 12.
The scale gets its name from the two men who developed it civil engineer Herbert Saffir and meteorologist Bob Simpson. Hurricanes form near the Equator generally between 5 and 20 degrees latitude but never right on the Equator. Winds 74-95 mph 119-153 kmhr Category 2.
The Beaufort scale is still used today to estimate wind strengths. Hurricanes always form over the warm waters of the tropical oceans and generally where the sea-surface temperature exceeds 265C 76F. The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale is a 1 to 5 rating or category based on a.
Once a tropical cyclone reaches maximum sustained winds of 74 miles per hour or higher it is then classified as a hurricane typhoon or tropical cyclone depending upon where the storm originates in the world. Any storm that reaches a sustained wind speed of 74 miles per hour is called a hurricane When a storm becomes a hurricane it retains the name that it was given as a tropical storm. In the North Atlantic central North Pacific and eastern North Pacific the term hurricane is used.
He developed the scale in 1805 to help sailors estimate the winds via visual observations. Fulltriple-fullfull an acrobatic maneuver consisting of three flips and five twists with one twist on the first flip three twists on the second flip one twist on the third flip. One of the first scales to estimate wind speeds and the effects was created by Britains Admiral Sir Francis Beaufort 1774-1857.
Technically the system is called a tropical storm if wind speeds are between 34 and 63 knots and it is only classified as a hurricane in the wind speed exceeds 63 knots. There are five levels of the scale known as categories. A hurricane is on average 500 miles wide and 10 miles high and moves forward like an enormous spinning top at a typical speed of 17 knots.
Tap again to see term. Fran was the sixth named storm of the 1996 hurricane season. Those with maximum sustained winds of 39 mph or higher are called tropical storms.
The Hurricane Severity Index HSI is another scale used and rates the severity of all types of tropical and subtropical cyclones based on both the intensity and the size of their wind fields. Click card to see definition. It classifies hurricanes by their wind intensity.
The scale measures the wind-speeds to determine the intensity of the hurricane. The Saffir-Simpson scale is used to measure the strength of hurricanes in the North Atlantic Ocean and the northeastern Pacific Ocean. Hurricanes are measured on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale which runs from Category 1 up to Category 5.
Tap card to see definition. Winds 119-153 kmhr 74-95 mph -. The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale estimates potential property damage.
It was so destructive that the name Fran was retired from use. The Enhanced Fujita Scale or EF Scale which became operational on February 1 2007 is used to assign a tornado a rating based on estimated wind speeds and related damage. Meteorologists use the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale to classify hurricanes into categories one to five.
When tornado-related damage is surveyed it is compared to a list of Damage Indicators DIs and Degrees of Damage DoD which help estimate better the range of wind speeds the tornado likely produced. The HSI is a 0 to 50 point scale allotting up to 25 points for a tropical cyclones intensity and up to 25 points for wind field size. The initial scale was developed by Herbert.
A category five hurricane has wind speeds that exceed 252 kilometers 157 miles per hour. NASAs Hurricane Web page uses the official NOAA measurements in its tropical cyclone coverage. The scale is called the SaffirSimpson Hurricane Scale.
Although this was easy for meteorologists to track it was widely seen as confusing for the. The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale is a 1 to 5 rating based only on a hurricanes maximum sustained wind speed. Categories three to five are considered a major storm.
National Hurricane Center NHC. Ingredients for a hurricane. Classification of Hurricanes.
Tap card to see definition. This scale does not take into account other potentially deadly hazards such as storm surge rainfall flooding and tornadoes. The Saffir-Simpson hurricane scale was originally created to help people decide how they should respond to storms.

The Saffir Simpson Scale For Hurricanes And Hal Sey S Scale For Download Table
The Saffir Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale And Why It Matters In Florida Hurricane Damage
Saffir Simpson And Sensibility Hurricane Risk Miscommunication
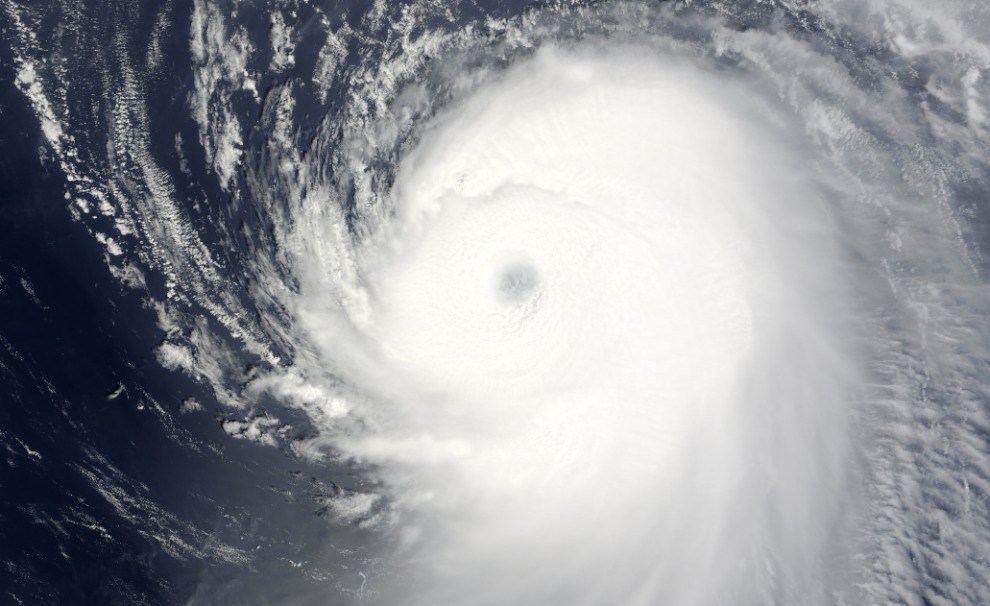

Saffir Simpson Hurricane Scale U S National Park Service

Is It Time To Scrap The Saffir Simpson Hurricane Rating Scale By Paul Douglas Medium
Surface Pressure A Better Indicator Of Hurricane Damage Potential New Study Says The Weather Channel Articles From The Weather Channel Weather Com
How Are Atlantic Hurricanes Ranked The Saffir Simpson Scale Smos Wind Data Service Storm Projects
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/7238885/scale.png)
How Do Hurricanes Form A Step By Step Guide Vox
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/9115467/harvey_goes_82517.jpg)
How Do Hurricanes Form A Step By Step Guide Vox
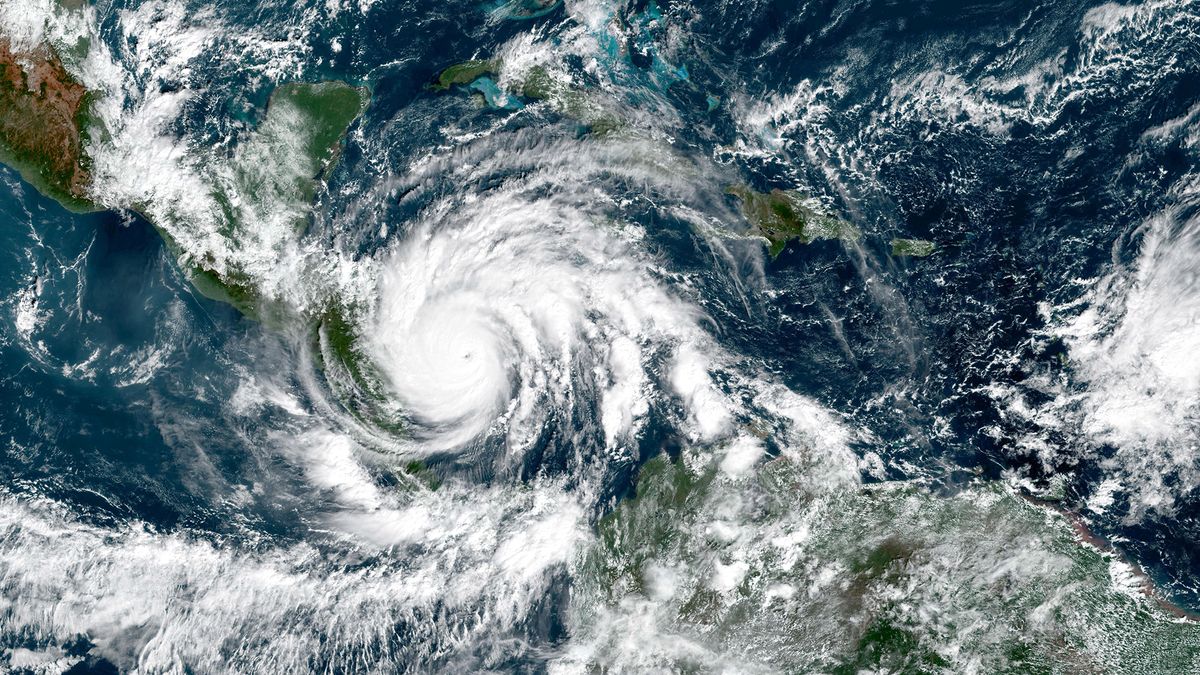

Hurricane Season 2021 How Long It Lasts And What To Expect Live Science

Hurricane Cyclone Typhoon Differences True North Marine

Evolving The Saffir Simpson Hurricane Categories By Jim Williams Medium

What Is The Saffir Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale Accuweather

All You Need To Know About Hurricane Categories Damage Potential Riot Glass



Comments
Post a Comment